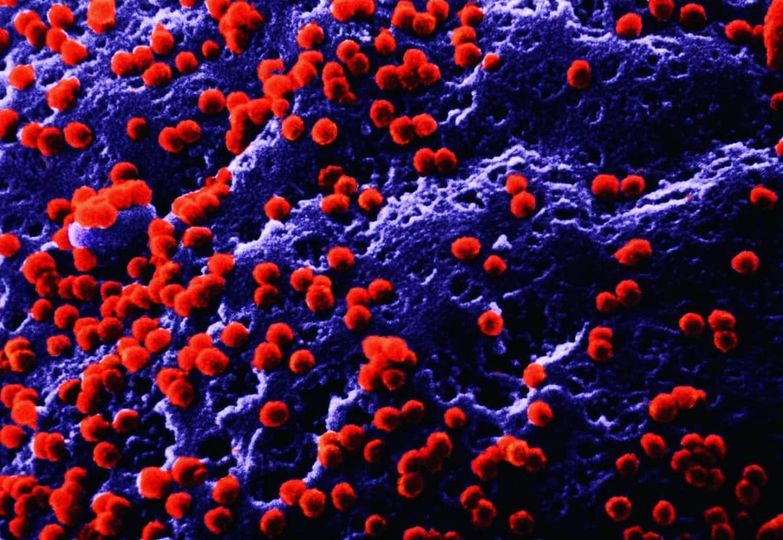
AIDS virus particles budding from the surface of a T4 lymphocyte cell. - AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) is a disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). HIV infects T4 lymphocytes, and uses its own cellular machinery to make more copies of HIV. These copies then burst out of the cell, killing it and infecting others. T4 lymphocytes are white blood cells, and an important part of the immune system. AIDS severely damages the immune system, making normally harmless infections potentially fatal. Magnification x130,000.
.png)
.png)